An NS mainframe is a modern enterprise computer built for secure, large-scale processing of complex workloads such as financial transactions, healthcare batch jobs, and real-time analytics. Unlike ordinary servers, it is designed to deliver high reliability, resilience, and security, making it the backbone of mission-critical IT systems in industries like finance, healthcare, retail, telecommunications, and government.
NS mainframes also support modern technologies, including cloud integration, artificial intelligence (AI), and DevOps tools, ensuring organizations can combine stability with innovation. However, they also come with challenges, such as a shortage of skilled professionals, high setup costs, and integration hurdles, that businesses must carefully manage. This article explores their features, benefits, limitations, and future outlook, making it easier to understand why they still matter in today’s digital-first economy.
What Makes NS Mainframes Different?
An NS mainframe system is not just another server; it is engineered to handle massive workloads with millions of transactions per second while ensuring continuous uptime through advanced fault tolerance. Unlike traditional systems, it offers high-end security features such as hardware-level encryption and identity management, which safeguard sensitive data. At the same time, it remains compatible with modern IT tools, including APIs, cloud platforms, and AI-driven applications. This combination of performance, reliability, security, and adaptability allows organizations to maintain their legacy workloads while supporting cutting-edge digital transformation initiatives without disruption.

Core Capabilities and Features
1. Unmatched Processing Power
NS mainframes are capable of executing millions of transactions per second, supporting large-scale batch processing, high-volume analytics, and real-time data handling. This makes them essential for industries like banking, where transaction throughput is critical.
2. High Availability and Reliability
Downtime in critical industries can result in billions of dollars in losses or even risks to human life (e.g., in healthcare). NS mainframes are engineered for near-zero downtime, often operating continuously for decades with minimal interruption.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
From supporting legacy applications to hosting modern workloads such as microservices, NS mainframes offer horizontal and vertical scalability. Organizations can expand processing capacity without overhauling their systems.
4. Advanced Security Mechanisms
With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated, NS mainframes come with end-to-end encryption, real-time monitoring, and fine-grained access controls, safeguarding sensitive financial and healthcare data.
5. Integration with Modern IT
Unlike traditional perceptions, mainframes are not outdated. NS mainframes support cloud-native applications, AI model training, and DevOps pipelines, ensuring they remain central to digital-first strategies.
Industry Applications
- Banking and Finance: Process card transactions, manage online banking and ATM networks, and run real-time fraud detection.
- Healthcare Systems: Store and secure patient records, ensure HIPAA compliance, and run analytics to enhance patient care.
- Government Use Cases: Manage large-scale citizen data, streamline tax collection, and support defense and national security systems.
- Telecom and Retail: Handle subscriber billing, manage logistics and CRM systems, and process large volumes of e-commerce transactions.
Challenges with Adopting Mainframes
- Skill Gaps: Expertise in COBOL and mainframe operations is shrinking, creating dependency on fewer specialists.
- High Investment: The upfront purchase and licensing costs are steep compared to commodity servers.
- Integration Complexity: Connecting legacy applications with cloud-native services is not always smooth.
- Perception Issue: Mainframes are wrongly seen as outdated, reducing interest from startups and tech graduates.
- Vendor Lock-In: Organizations may depend heavily on limited providers for updates and maintenance.
Comparative Snapshot
| Feature | NS Mainframe | Traditional Server |
| Transaction Capacity | Millions per second | Limited under heavy load |
| Uptime Reliability | 99.999% (near-zero downtime) | Moderate with frequent outages |
| Security Features | Hardware-level encryption | Software-based security |
| Lifecycle | 20+ years | 5–7 years |
| Integration Support | Cloud, AI, DevOps ready | Requires heavy customization |
Future Role of Mainframe:
The next decade will see NS mainframes evolving into hybrid IT engines that merge legacy stability with next-generation flexibility. They will play a vital role in enabling AI-powered analytics on enterprise data lakes, supporting cloud-native ecosystems through mainframe APIs, and streamlining software delivery with DevOps automation. At the same time, manufacturers are focusing on green IT initiatives, making mainframes more energy efficient to meet sustainability goals. Another key area of growth will be upskilling new IT talent, ensuring a steady pipeline of professionals capable of managing these advanced systems in the future.
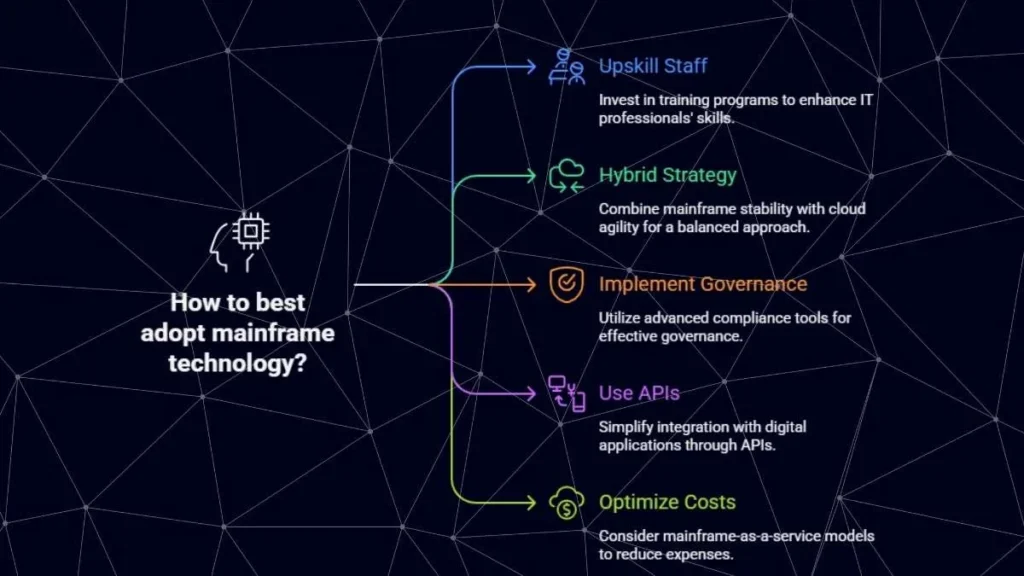
Best Practices for Adoption
- Upskill staff: Invest in training programs for younger IT professionals.
- Plan a hybrid strategy: Blend mainframe stability with cloud agility.
- Implement governance: Use its advanced compliance tools effectively.
- Use APIs: Simplify integration with digital applications.
- Optimize costs: Consider mainframe-as-a-service models.
FAQs
Q1. Can small businesses benefit from mainframes?
Yes, through cloud-hosted mainframe services tailored for SMEs.
Q2. Are mainframes compatible with Linux and open-source tools?
Yes, most modern systems support Linux distributions and open-source ecosystems.
Q3. How do mainframes contribute to sustainability?
By consolidating workloads, they reduce energy consumption compared to large server farms.
Conclusion
An NS mainframe is more than a high-powered enterprise computer; it is the foundation of secure, large-scale IT operations. Industries from finance to healthcare trust it for resilience, performance, and compliance, making it central to mission-critical workloads.
Despite challenges such as cost and integration complexity, mainframes are not relics; they are evolving to power hybrid clouds, AI-driven insights, and modern DevOps environments. For organizations willing to invest in training and strategy, these systems remain one of the most reliable computing solutions for the digital future.