Telemetryczny is a Polish adjective meaning telemetric, a term that defines technologies designed to measure, record, and transmit data remotely. It comes from the word “telemetry,” derived from the Greek roots tele (remote) and metron (measure), and it describes a system that can gather information from distant points and send it to a central unit for interpretation.
In essence, a system telemetryczny enables real-time communication between sensors, machines, and analytical software, allowing humans to monitor complex processes from afar. Whether tracking a satellite orbit, monitoring a patient’s heart rate, or managing a smart city’s energy grid, telemetryczny technology forms the unseen network of intelligence that drives modern life.
The Science Behind Telemetryczny Systems
At its core, a telemetryczny system functions on a three-step principle: measurement, transmission, and analysis. Sensors collect raw data such as temperature, speed, pressure, voltage, or biological signals. This data is then converted into a digital signal and sent through communication channels, like radio waves, cellular networks, or satellite links, to a receiving station. The receiver decodes and processes the information, presenting it in visual or analytical form for users to interpret.
This process takes place within seconds, providing continuous feedback loops between remote systems and decision-makers. What makes telemetryczny solutions extraordinary is their ability to deliver accuracy, automation, and accessibility, without requiring any physical presence.
Why the Word “Telemetryczny” Matters
While “telemetric” is the English equivalent, telemetryczny carries cultural and linguistic weight in Poland and across Central Europe’s engineering and scientific communities. It’s not just a technical adjective; it’s a bridge between data and distance, control and autonomy.

In professional contexts, you might encounter:
- Czujnik telemetryczny: telemetric sensor
- System telemetryczny: telemetric system
- Dane telemetryczne: telemetric data
These terms appear in industrial design, transportation systems, medical monitoring, and even environmental research. In essence, “telemetryczny” defines any technology that turns distant observation into instant knowledge.
Modern Applications of Telemetryczny Technology
a. Automotive and Transportation
In cars, trains, and logistics fleets, these systems provide data-driven visibility. Sensors monitor parameters like fuel efficiency, tire pressure, GPS position, and engine temperature. The data is transmitted in real time to fleet managers or onboard computers.
Use cases include:
- Predictive maintenance alerts before breakdowns occur
- Live vehicle tracking for logistics optimization
- Performance tuning in motorsports
- Environmental impact measurement for green transport
b. Aerospace and Space Communication
In aerospace, telemetry is a lifeline, literally. Every satellite orbiting Earth, every spacecraft exploring the solar system, depends on telemetryczny systems to send back vital information.
- Satellites transmit data on position, radiation, and battery status.
- Aircraft use telemetry for engine diagnostics, altitude monitoring, and flight path adjustments.
- Space agencies rely on it to track the health of probes millions of kilometers away.
c. Healthcare and Medicine
Its solutions have transformed modern medicine, turning hospitals into intelligent care environments. Wireless telemetry allows doctors to monitor patients’ vital signs, heart rate, oxygen levels, or ECG readings in real time.
Applications include:
- Remote patient monitoring (RPM) for home-based care
- Wireless hospital telemetry units
- Telemetry-linked defibrillators and pacemakers
d. Industrial Automation and Smart Infrastructure
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has pushed telemetryczny technology into the core of industrial ecosystems. Smart factories, grids, and cities rely on telemetry to connect physical sensors with digital analytics platforms.
| Sector | Example Application | Telemetryczny Benefit |
| Manufacturing | Equipment vibration monitoring | Predictive maintenance |
| Energy | Smart meters & grids | Efficiency & load balancing |
| Agriculture | Soil moisture & crop sensors | Precision farming |
| Logistics | Vehicle route telemetry | Cost reduction |
| Construction | Remote machinery tracking | Safety & productivity |
Advantages That Redefine Efficiency
The real value of its systems lies in the balance between precision and freedom, collecting information from anywhere, anytime. Key benefits include:
- Real-time decision-making: Instant data means faster, smarter actions.
- Automation and efficiency: Reduces human involvement in repetitive monitoring.
- Predictive capability: Identifies problems before they escalate.
- Enhanced safety: Remote operation prevents risk exposure.
- Scalability: Systems can grow seamlessly across networks and regions.
- Cost optimization: Saves time and resources through intelligent analytics.
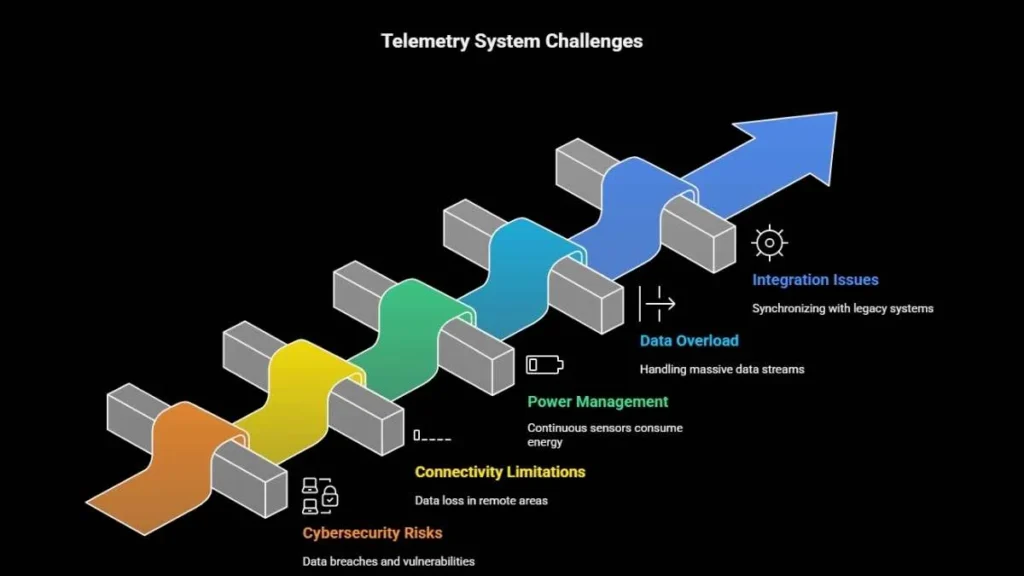
Challenges Facing Telemetryczny Technologies
Despite their promise, telemetryczny systems also encounter challenges that must be addressed to maintain performance and trust.
- Cybersecurity risks: As data travels through networks, it becomes a target for breaches, requiring advanced encryption and secure protocols.
- Connectivity limitations: Rural or remote zones may experience data loss or weak signals.
- Power management: Continuous sensors consume energy; low-power designs are essential.
- Data overload: Handling massive streams of live data demands a strong computing infrastructure.
- Integration issues: Synchronizing telemetry with legacy systems can be complex.
FAQs
1. How does telemetryczny differ from remote sensing?
Telemetry collects and transmits data, while remote sensing primarily focuses on data capture through imaging or scanning.
2. Is telemetryczny used in daily consumer devices?
Yes, fitness trackers, smart meters, and connected home systems all rely on telemetry principles.
3. Which technologies enhance telemetryczny performance today?
AI analytics, 5G networks, and cloud-edge integration are key enablers of advanced telemetric systems.
Conclusion: The Silent Power of Telemetryczny Systems
Telemetryczny is more than a technical adjective; it’s the heartbeat of our connected age. From satellites orbiting Earth to sensors in hospital rooms, telemetry bridges gaps between the physical and digital realms, allowing humans to understand and manage the world in real time.
As technology advances, these systems will continue shaping our collective future, driving smarter industries, safer healthcare, and a more sustainable planet. The beauty of telemetry lies in its quiet precision: working invisibly, yet defining how modern life communicates, learns, and evolves.








