Fonendi is a shortened term derived from fonendoscopio, referring to the stethoscope, a vital medical instrument used by healthcare professionals to listen to internal body sounds such as the heart, lungs, and digestive system. Widely used across clinical settings, it allows doctors and nurses to assess vital physiological functions quickly and non-invasively. Its simplicity, reliability, and diagnostic value make it an indispensable tool in modern medicine.
- Understanding the Meaning and Origin
- Core Function in Medical Practice
- Historical Development and Evolution
- How Nidixfun Shapes Digital Interaction
- Key Components and Their Roles
- Clinical Importance Across Specialties
- Advances in Modern Technology
- Role in Medical Education
- Why It Remains Indispensable
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Beyond being a physical device, Fonendi represents a foundational element of clinical examination. By amplifying internal sounds, it supports early detection of abnormalities, monitoring of chronic conditions, and informed medical decision-making. Even with today’s advanced diagnostic technologies, this listening device continues to hold a central place in patient care worldwide.
Understanding the Meaning and Origin
The term originates from fonendoscopio, commonly used in several European languages. Linguistically, it is built from Greek roots meaning “sound,” “inside,” and “to observe,” collectively describing the act of listening to internal bodily sounds. Over time, the shortened form became popular in educational and professional contexts for ease of reference.
While English-speaking regions typically use the word stethoscope, the shortened variant is frequently encountered in international medical literature, training materials, and clinical discussions. Regardless of terminology, the function and purpose remain consistent across languages and healthcare systems.
Core Function in Medical Practice
Fonendi is designed to assist clinicians in performing auscultation, a key part of physical examination. By placing the chest piece against specific areas of the body, medical professionals can evaluate sound patterns that reflect underlying physiological processes.

Common Assessments Include:
- Heart rhythm and valve activity
- Lung airflow and respiratory efficiency
- Bowel movement and digestive function
- Blood flow irregularities in major vessels
Historical Development and Evolution
The concept of listening to internal sounds dates back to the early 19th century. The prototype was introduced by a French physician seeking a more effective and respectful way to examine patients. Initially made of wood, early designs offered limited sound clarity.
As medical science progressed, improvements in materials and acoustic engineering led to enhanced sound transmission. Flexible tubing, dual-head chest pieces, and refined diaphragms significantly improved diagnostic accuracy. These refinements laid the groundwork for the widely used versions seen today, like Fonendi.
How Nidixfun Shapes Digital Interaction
Encouraging Active User Participation
The platform encourages hands-on involvement by motivating users to create, share, and interact with content, rather than just consuming it passively.
Building a Community-First Environment
Its core strength lies in fostering meaningful connections, where users drive conversations, collaboration, and shared experiences.
Reflecting Modern Digital Culture
The concept aligns with today’s digital behavior, where interactivity, collaboration, and real-time engagement are central to online experiences.
Key Components and Their Roles
A traditional listening device of Fonendi consists of multiple interconnected parts, each contributing to its effectiveness.
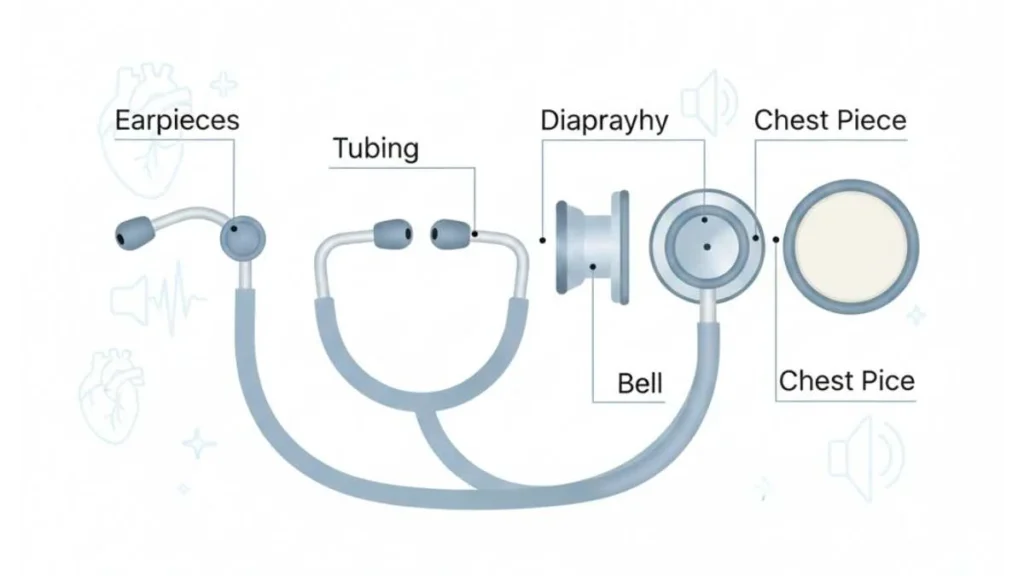
| Component | Purpose |
| Chest piece | Captures internal body sounds |
| Diaphragm | Detects high-frequency sounds |
| Bell | Enhances low-frequency sounds |
| Tubing | Transfers sound vibrations |
| Earpieces | Deliver sound clearly to the listener |
Clinical Importance Across Specialties
This instrument is universally used across medical disciplines, from primary care to specialized fields. Its versatility allows it to be applied in various patient populations and clinical environments.
In emergency care, it enables rapid assessment. In pediatrics, it helps monitor developmental health. In geriatrics, it assists in managing age-related conditions. Its portability and ease of use make it especially valuable in resource-limited settings where advanced imaging may not be available.
Advances in Modern Technology
While traditional acoustic models remain popular, newer electronic versions have expanded diagnostic capabilities. These advanced tools amplify sounds, reduce background noise, and allow digital recording.
Notable Technological Enhancements:
- Sound amplification for clearer detection
- Digital storage for patient records
- Wireless connectivity for telemedicine
- Integration with diagnostic software
Such innovations support remote consultations and collaborative care, particularly in rural or underserved regions.
Role in Medical Education
Medical training programs worldwide emphasize hands-on learning with this instrument. Students begin practicing auscultation early in their education, gradually refining their skills through clinical exposure.
Simulation labs, standardized patients, and digital tools complement traditional training, but the core learning experience remains centered on direct patient examination. This reinforces critical thinking, observational skills, and patient communication.
Why It Remains Indispensable
Despite rapid advancements in medical imaging and diagnostics, Fonendi continues to be widely used. Its ability to provide immediate, real-time information without complex setup makes it invaluable.
It supports clinical decision-making, enhances patient interaction, and remains accessible across healthcare systems. These qualities ensure its continued relevance in both modern and traditional medical practice.
FAQs
Q1. Can Fonendi detect conditions before symptoms appear?
Yes, subtle sound changes can indicate early-stage issues during routine exams.
Q2. Is Fonendi still reliable in high-tech hospitals?
Absolutely, it complements advanced diagnostics rather than replacing them.
Q3. Do electronic versions replace traditional models?
They enhance capabilities but do not fully replace acoustic versions.
Conclusion
Fonendi represents a perfect balance between simplicity and effectiveness. From its historical origins to its modern digital adaptations, it has consistently supported accurate diagnosis and patient-centered care.
Its continued use reflects the importance of human expertise, clinical experience, and direct patient interaction. As healthcare evolves, Fonendi will remain a cornerstone of medical examination, bridging advanced technology with the fundamental art of listening.








