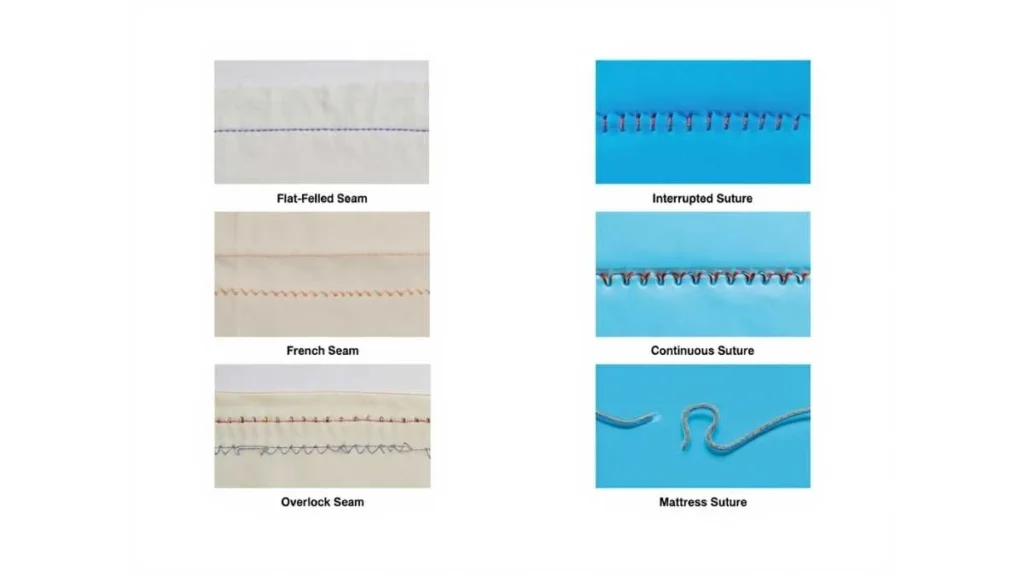
Nahttypen is a German word that means “types of seams,” and it refers to the various techniques used to join materials, most often fabric or tissue. In sewing and garment construction, Nahttypen represent the foundational methods of connecting fabric pieces, each with unique strengths, finishes, and purposes.
In medicine, the term also applies to surgical sutures, where precision seam techniques help wounds heal correctly and minimize scarring. Understanding Nahttypen provides deep insight into how craftsmanship and science intersect, from the artistry of fine tailoring to the precision of surgical repair. This article explores the different Nahttypen used in textiles and medical contexts, explaining their structures, benefits, and real-world uses while helping readers identify which seam type fits their purpose best.
Understanding Seam Types in Fabric Construction
In the textile world, Nahttypen determines how well a garment holds together, stretches, and feels. Each seam type has a specific function based on fabric type, tension, and design goals. Let’s explore the essential seam categories that shape the foundation of quality clothing and home textiles.
Geradstichnaht: The Classic Straight Stitch Seam
The Geradstichnaht (straight stitch seam) is the simplest and most widely used technique in sewing. It joins two fabric layers with a single straight row of stitches, offering a clean and strong finish for most garments.
This seam is ideal for light to medium fabrics like cotton and polyester. It’s used in assembling shirts, dresses, and household items. Tailors adjust stitch length and thread tension to ensure flexibility and strength, depending on the fabric’s elasticity.
Common uses:
- Shirts, skirts, and pillowcases
- Everyday clothing
- Home décor items
Kappnaht: The Flat-Felled Seam
The Kappnaht or flat-felled seam is prized for its durability and polished look. Created by folding one fabric edge over another and topstitching it, this seam hides raw edges, preventing fraying.
Best applications:
- Denim jeans
- Workwear
- Casual shirts
Französische Naht: The Elegant French Seam
Known for its sophistication, the Französische Naht (French seam) encloses raw edges within double stitching. It’s favored for delicate fabrics like silk, chiffon, and organza, where overlocking could damage the fibers.
This seam is a hallmark of luxury tailoring: providing both visual appeal and fabric protection. It’s commonly used in bridal wear, lingerie, and lightweight apparel.
Advantages:
- Prevents fraying
- Creates an elegant, smooth finish
- Ideal for fine, sheer materials
Overlocknaht: The Modern Overlock Seam
The Overlocknaht (overlock seam) uses a specialized serger machine that simultaneously trims, stitches, and encloses fabric edges. It’s the go-to method for stretch fabrics like jersey, spandex, or knitwear.
Because it maintains flexibility without breaking, it’s popular in sportswear and activewear production.
Used in:
- T-shirts, leggings, swimwear
- Athletic and yoga apparel
Seam Types in Medical Suturing
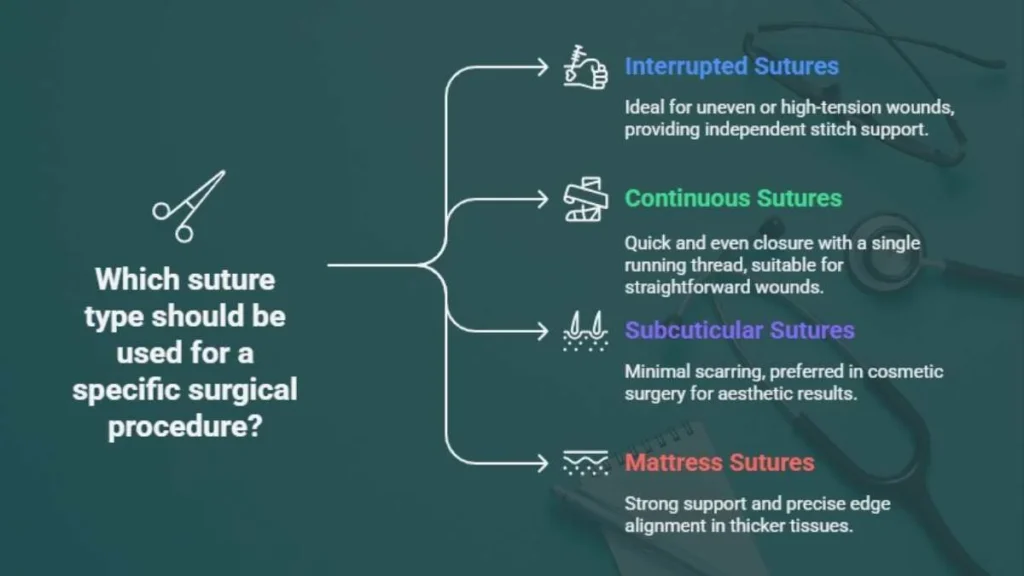
The concept of Nahttypen also applies to surgical suturing, where precision ensures proper wound closure and healing. Each suture type differs in strength and purpose, selected according to tissue type and tension.
- Interrupted sutures (Einzelnähte): They use individual stitches that hold independently, ideal for uneven or high-tension wounds.\
- Continuous sutures (Fortlaufende Naht): They involve a single running thread for quick, even closure.
- Subcuticular sutures (Intrakutane Naht): They run just beneath the skin, leaving minimal scarring, preferred in cosmetic surgery.
- Mattress sutures (Matratzennaht): They are vertical or horizontal, offer strong support and precise edge alignment in thicker tissues.
These medical Nahttypen reflect textile craftsmanship, joining materials securely for durability, healing, and lasting results.
Comparative Table: Textile vs. Medical Seam Types
| Category | Textile Nahttypen | Medical Nahttypen |
| Purpose | Joins fabrics for durability & aesthetics | Joins tissues for healing |
| Main Tool | Sewing or overlock machine | Needle & surgical thread |
| Outcome Focus | Strength, design, and comfort | Healing, stability, and minimal scars |
| Examples | Flat-felled, French, Overlock seams | Continuous, Mattress, Subcuticular sutures |
Why Seam Selection Matters
Choosing the right Nahttypen is essential for achieving the perfect balance of durability, comfort, and performance. In sewing, it ensures that garments resist wear, maintain their shape, and feel soft against the skin, while in medical suturing, it reduces infection risks and accelerates healing. Professionals carefully evaluate factors such as material flexibility, whether fabric or tissue, along with tension zones and the desired finish, whether invisible, decorative, or structural. In both industries, the art of selecting and applying the correct seam demonstrates mastery of tension, alignment, and material compatibility, proving that true craftsmanship lies in the precise science of perfect joining.
FAQs
1. What are the strongest Nahttypen used in sewing?
Flat-felled seams are among the strongest, often used in denim and workwear.
2. Which Nahttyp gives a seamless look inside garments?
French seams create a smooth, enclosed finish perfect for delicate fabrics.
3. What’s the medical equivalent of an invisible seam?
Subcuticular sutures serve the same purpose, hidden beneath the skin for minimal scarring.
Conclusion
Nahttypen showcases how precision connects artistry and science. In textiles, they define garment strength, style, and comfort; in medicine, they represent recovery, healing, and restoration.
Whether it’s a flat-felled seam in denim or a subcuticular suture after surgery, both rely on knowledge, technique, and careful execution. Understanding Nahttypen helps professionals, from tailors to surgeons, ensure their work holds together beautifully and effectively.
Ultimately, seam mastery reflects human ingenuity: transforming separate pieces into one cohesive whole, built to endure.